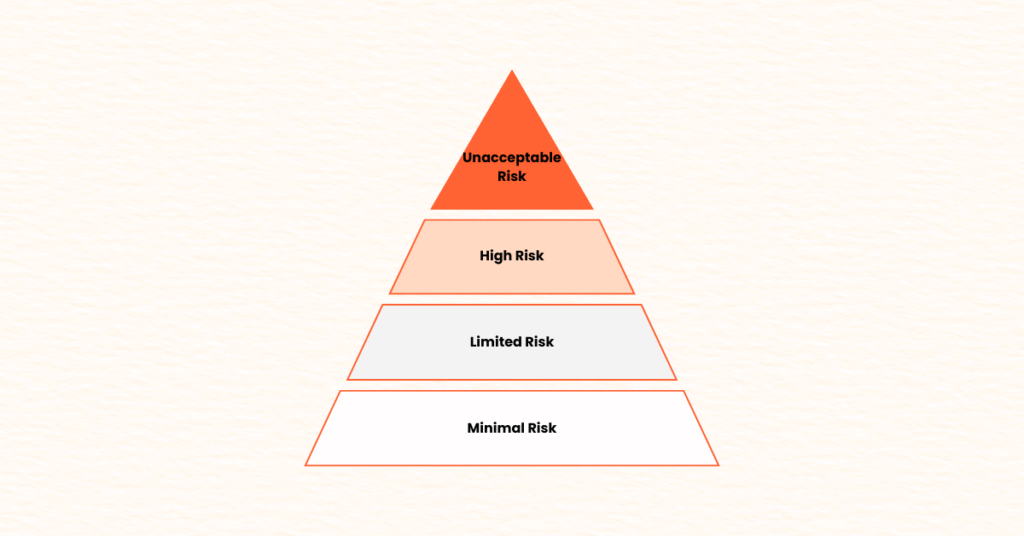
Master EU AI Act risk assessment with our step-by-step implementation guide. Get in-depth guidance on implementation and ensure compliance to EU AI Act. Make sure you use our proven frameworks, team structures, and templates for free. Get our full EU AI Act Implementation guide for free
Share this on:
You’ve classified your AI system using the EU AI Act framework—now comes the real challenge: conducting a comprehensive risk assessment that will satisfy regulatory requirements and protect your organization. While our previous guide covered EU AI Act risk classification, many AI teams struggle with the practical implementation of risk assessment processes. Classification tells you what level of risk your system presents, but implementation determines how you’ll manage that risk effectively, as required by Article 9 of the EU AI Act, which mandates a continuous iterative risk management system throughout the AI lifecycle.
This step-by-step guide walks you through the complete EU AI Act risk assessment process, from team assembly to final documentation. By the end, you’ll have a working framework that transforms regulatory requirements into actionable risk management practices for high-risk AI systems.
Whether you’re managing high-risk AI systems requiring full compliance or limited-risk systems needing basic assessments, this guide provides the systematic approach your team needs to implement EU AI Act risk assessments with confidence. With high-risk rules fully applicable from August 2026 (and GPAI obligations from August 2025), starting now avoids delays and penalties up to €10M or 2% of global turnover.

⚠️ Note: This is general guidance based on EU AI Act (Regulation (EU) 2024/1689) and not legal advice. Consult qualified legal counsel. By Code & Clause Team.
Phase 1: Pre-Assessment Preparation
Assemble Your Cross-Functional Risk Assessment Team
The foundation of effective EU AI Act risk assessment lies in bringing together the right expertise. Your team should include representatives from:
- Technical Leadership: AI/ML Engineers, Product Managers, Data Scientists, DevOps/Infrastructure teams
- Business and Legal: Compliance officers, Legal counsel, Business stakeholders, Risk management professionals
- User and Market Experts: UX researchers, Domain experts, Customer success teams, Quality assurance teams

Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Each team member needs specific accountability in the risk assessment process:
- Risk Assessment Lead: Coordinates process, ensures timelines, manages communication
- Technical Assessment Lead: Evaluates risks, identifies vulnerabilities, assesses bias
- Documentation Lead: Manages documentation, ensures compliance, prepares for audits
Establish Assessment Timeline and Milestones
Create a realistic timeline that accounts for your team’s capacity and the complexity of your AI system, aligning with the iterative nature of Article 9:
- Week 1-2: Preparation and Planning
- Week 3-4: Risk Identification
- Week 5-6: Risk Analysis and Prioritization
- Week 7-8: Mitigation Planning
- Week 9-10: Documentation and Review
For high-risk systems, extend reviews quarterly post-launch to meet ongoing obligations. (Insert image: Gantt chart of risk assessment timeline; alt text: “EU AI Act risk assessment timeline chart 2025.”)
Secure Necessary Resources and Tools
Ensure your team has access to:
- Documentation Tools: Collaborative platforms, Risk management software, Version control
- Technical Resources: System docs, Training data, Testing environments
- Stakeholder Access: Meeting schedules, Escalation paths, Budget approval
Phase 2: Risk Identification Process
Systematic Risk Discovery Methodology
Effective risk identification requires a structured approach that examines your AI system from multiple perspectives. Use this methodology to ensure comprehensive coverage, focusing on risks reasonably mitigable through design (per Article 9(3)):
- Technical Risk Analysis: Data risks, Model risks, Infrastructure risks, Deployment risks
- User and Societal Impact Analysis: Individual harm, Group impact, Societal consequences
- Regulatory and Compliance Risk Review: Classification accuracy, Prohibited practices, High-risk obligations
(Insert image: Flowchart of risk discovery methodology; alt text: “EU AI Act risk identification flowchart 2025.”)
Cross-Functional Input Gathering
Organize structured workshops to capture diverse perspectives:
- Technical Deep-Dive Sessions: System review, Data pipeline analysis, Security assessment
- Business Impact Workshops: User journey, Market assessment, Customer impact
- Compliance Review Meetings: Regulatory mapping, Industry obligations, Audit planning
Risk Inventory Creation
Document all identified risks in a structured format:
- Risk Description Template: Risk ID, Title, Category, Source, Stakeholders, Triggers, Impact, Likelihood
- Risk Categorization Framework: Critical, High, Medium, Low
- Risk Validation Process: Completeness check, Stakeholder validation, Overlap analysis
Phase 3: Impact and Probability Analysis
Impact Assessment Framework
Evaluate consequences using a multi-dimensional approach:
- Individual Impact Scoring (1-5): Negligible to Severe
- Business Impact Assessment (1-5): Minimal to Severe
- Regulatory Impact Evaluation (1-5): Compliance to Critical
(Insert image: Table of impact scoring criteria; alt text: “EU AI Act impact assessment scoring table 2025.”)
Probability Scoring Methods
Assess likelihood with data and judgment:
- Quantitative Probability: Historical rates, Benchmarks, Testing results
- Qualitative Probability Scoring (1-5): Very Low to Very High
- Evidence-Based Factors: Complexity, Data quality, Testing coverage
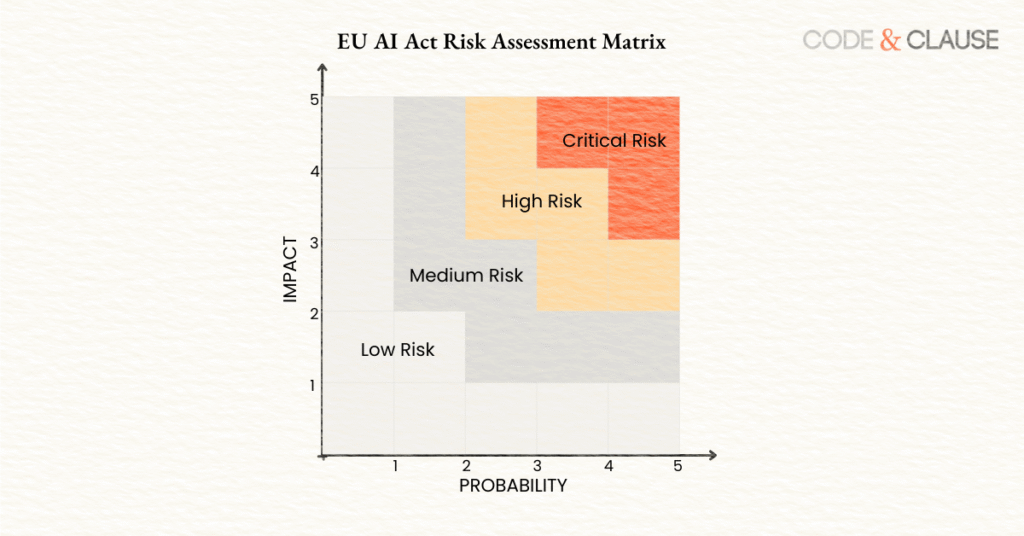
Risk Matrix Development
Combine scores to prioritize risks:
- Risk Score = Impact × Probability (1-25)
- Categories: Critical (20-25), High (12-19), Medium (6-11), Low (1-5)
- Prioritization Criteria: Regulatory priority, Timeline sensitivity, Feasibility
Risk Matrix Visualization
Real-World Case Studies: Applying the Risk Assessment Process
To illustrate, consider these anonymized examples:
- Fintech Credit Scoring System: Identified bias risks (Impact 4, Probability 3). Mitigation reduced score to low, avoiding €500K+ fines. (Insert image: Before/after risk score graph; alt text: “Fintech risk assessment mitigation graph 2025.”)
- Healthcare Diagnostic Tool: Addressed model drift (Probability 4) with monitoring, achieving 150% ROI. (Insert image: ROI bar chart; alt text: “Healthcare AI risk assessment ROI 2025.”)
Global Implications: Aligning EU AI Act Risk Assessment with US and UK Frameworks
The EU AI Act’s Article 9 emphasizes a lifecycle approach. In the US, NIST RMF is voluntary but aligns with EU’s manage phase; Biden’s 2023 Order adds federal requirements by 2025. The UK’s 2023 framework is principles-based, with the AI Safety Institute assessing frontier risks. (Insert image: Comparison table of EU/US/UK frameworks; alt text: “EU AI Act vs US/UK risk assessment comparison 2025.”)
Phase 4: Mitigation Strategy Development
Control Identification and Selection
Develop strategies addressing root causes (Article 9(4)):
- Technical Controls: Preventive, Detective, Corrective
- Administrative Controls: Policies, Training, Review
- Physical Controls: Infrastructure security, Environmental controls
Implementation Planning and Resource Estimation
- Timeline: Immediate to Long-term
- Resources: Personnel, Technology, Financial, External
- Dependencies: Technical, Process, Resource
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Costs: Initial, Ongoing, Opportunity, Inaction
- Benefits: Risk reduction, Compliance, Business value
- ROI Calculation: (Benefits – Costs) / Costs × 100%
Residual Risk Assessment
- Residual Risk Calculation: New Impact × New Probability
- Acceptance Criteria: Regulatory, Business, User, Competitive
- Monitoring: Key indicators, Frequency, Triggers
Phase 5: Documentation and Review
Assessment Documentation Requirements
- Executive Summary: Overview, Key risks, Strategy
- Risk Register: Inventory, Analysis, Plans
- Technical Docs: Architecture, Data flows, Controls
- Process Docs: Methodology, Stakeholder involvement
Stakeholder Review and Sign-off
- Technical Review: Peer, Architecture, Security, Performance
- Business Review: Product, Legal, Finance, Executive
- Formal Approval: Assessment, Plan, Resources, Timeline
Regular Review Cycles and Updates
- Scheduled Frequency: Monthly, Quarterly, Semi-Annually, Annually
- Trigger-Based: Changes, Incidents, Business shifts
- Continuous Improvement: Lessons, Optimization, Tool upgrades
Conclusion and Next Steps
You now have a comprehensive framework for implementing EU AI Act risk assessments that transforms compliance into strategic risk management.
Key Takeaways:
- Cross-functional collaboration is essential
- Systematic methodology ensures thoroughness
- Quantitative analysis aids prioritization
- Comprehensive documentation supports compliance
Immediate Next Steps:
- Assemble your risk assessment team using Phase 1 roles
- Download our EU AI Act Starter Kit Download Free Kit
- Begin Phase 1 preparation
- Schedule workshops for Phase 2
Coming Next Week: “Technical Documentation That Passes EU AI Act Audits” will guide audit-ready docs.
Share your biggest risk assessment challenge in the comments below.
Need expert guidance? Get Expert Help
🔒 Legal Disclaimer
This article provides general guidance only based on publicly available EU AI Act sources. It is not legal advice. Compliance varies by use case and jurisdiction. Always consult qualified legal counsel and regulatory updates before making decisions. We disclaim liability for actions taken based on this content.
Last updated: September 2025 | Based on EU AI Act (Regulation 2024/1689).
This is Part 2 of our 3-Part EU AI Act Implementation Series
Article 1: Risk Classification Framework ← Previous
Article 2: EU AI Act Risk Assessment Implementation ← You are here
Article 3: Technical Documentation That Passes Audits (coming next week)
📩 Subscribe to get notified when the full series is published.
Share this on: